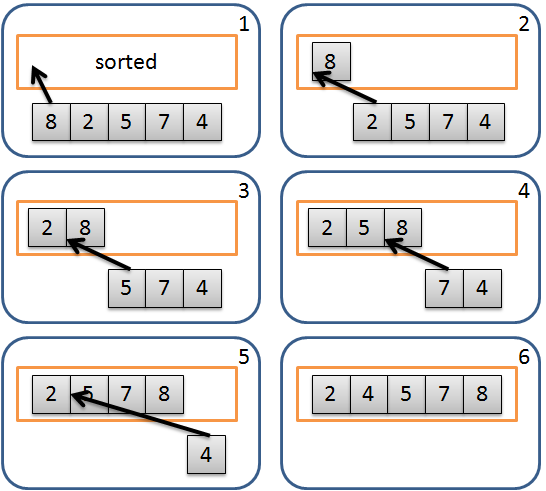
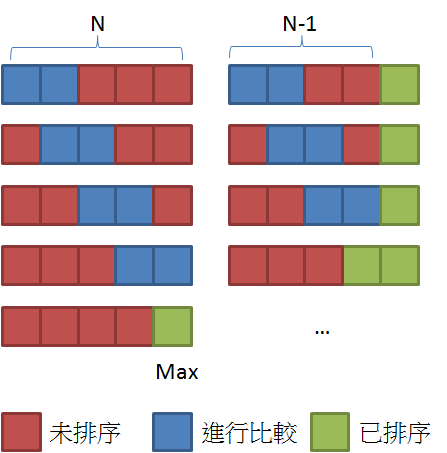
簡介 插入排序法 (Insertion Sort) 是排序演算法 的一種,他是一種簡單容易理解的排序演算法,其概念是利用另一個數列來存放已排序部分,逐一取出未排序數列中元素,從已排序數列由後往前找到適當的位置插入。運算流程如下:
從未排序數列取出一元素。 由後往前和已排序數列元素比較,直到遇到不大於自己的元素並插入此元素之後;若都沒有則插入在最前面。 重複以上動作直到未排序數列全部處理完成。 流程示意圖:
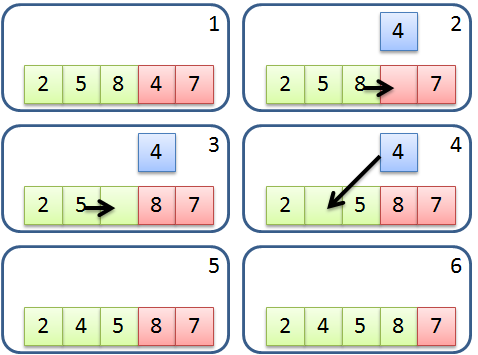
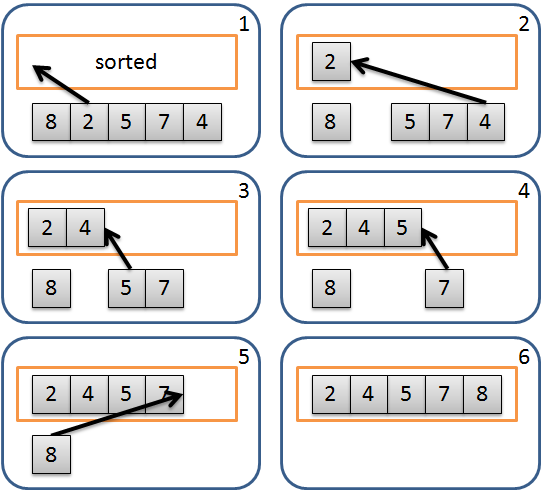
然而實作上通常不使用額外的數列來儲存已排序的部分,而使用原地 (In-place) 的方式來完成,數列的左半部表示已排序部分,右半部表示未排序部分,不另外使用數列。在與已排序的部分比較時,利用指派 (Assign) 的方式將元素往右位移,來達到插入的效果,因為位移的關係需要有另一個變數來暫存最右邊的數值。運算流程如下:
將未排序的部分最左邊元素儲存到暫存變數。 由後往前和已排序部分元素比較,若比自己大則將該元素往右邊位移。 重複2的動作直到遇到不大於自己的元素,將暫存變數寫入在該元素之後;若都沒有則寫入在最前面。 重複以上動作直到未排序部分全部處理完成。 流程示意圖:
分析 最佳時間複雜度:O(n) 平均時間複雜度:O(n^2) 最差時間複雜度:O(n^2) 空間複雜度:O(1) Stable sort:是 虛擬碼 額外空間版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function sort(list) var sorted = [] for i = 0;i < list.length;++i var n = list[i] var j = sorted.length - 1 while j >= 0 && sorted[j] > n --j end while n 插入至 sorted[j] 之後 end for list = sorted end function
In-place
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 function sort(list) for i = 1;i < list.length;++i var n = list[i]; // 比 n 大的往右移 for j = i - 1;j >= 0 && list[j] > n;--j list[j + 1] = list[j]; end for list[j + 1] = n; end for end function
語法 C# 額外空間版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;namespace InsertionSort { class ExtraSpace { public static void Sort (int [] array { List<int > sorted = new List<int >(array.Length); for (int i = 0 ; i < array.Length; ++i) { int n = array[i]; int index = sorted.Count - 1 ; while (index >= 0 && sorted[index] > n) --index; sorted.Insert(index + 1 , n); } sorted.ToArray().CopyTo(array, 0 ); } } }
In-place 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;namespace InsertionSort { class InPlace { public static void Sort (int [] array { int n, j; for (int i = 1 ; i < array.Length; ++i) { n = array[i]; for (j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 && array[j] > n; --j) array[j + 1 ] = array[j]; array[j + 1 ] = n; } } } }
Java 額外空間版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import java.util.List;import java.util.ArrayList;public class ExtraSpace { public static void Sort (int [] array) { List<Integer> sorted = new ArrayList <Integer>(array.length); for (int i = 0 ; i < array.length; ++i) { int n = array[i]; int index = sorted.size() - 1 ; while (index >= 0 && sorted.get(index) > n) --index; sorted.add(index + 1 , n); } for (int i = 0 ;i < array.length;++i) array[i] = sorted.get(i); } }
In-place 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class InPlace { public static void Sort (int [] array) { int n, j; for (int i = 1 ; i < array.length; ++i) { n = array[i]; for (j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 && array[j] > n; --j) array[j + 1 ] = array[j]; array[j + 1 ] = n; } } }
C++ 額外空間版本 ExtraSpace.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #ifndef EXTRASPACE_H #define EXTRASPACE_H #include <list> using namespace std;class ExtraSpace { public : static void Sort (int * array, int length) protected : private : }; #endif
ExtraSpace.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include "ExtraSpace.h" void ExtraSpace::Sort (int * array, int length) list<int > sorted; for (int i = 0 ; i < length; ++i) { int n = array[i]; list<int >::iterator iterator = sorted.begin (); while (iterator != sorted.end () && *iterator <= n) ++iterator; sorted.insert (iterator, n); } int i = 0 ; for (list<int >::iterator iterator = sorted.begin (); iterator != sorted.end () ;++iterator, ++i) array[i] = *iterator; }
In-place InPlace.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #ifndef INPLACE_H #define INPLACE_H class InPlace { public : static void Sort (int * array, int length) protected : private : }; #endif
InPlace.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 #include "InPlace.h" void InPlace::Sort (int * array, int length) int n, j; for (int i = 1 ; i < length; ++i) { n = array[i]; for (j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 && array[j] > n; --j) array[j + 1 ] = array[j]; array[j + 1 ] = n; } }
隨機產生 20000 筆資料實測
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 C# InPlace: 880ms ExtraSpace: 810ms Java InPlace: 115ms ExtraSpace: 319ms C++ InPlace: 840ms ExtraSpace: 2070ms
延伸閱讀 排序演算法 (Sorting)