簡介 快速排序法是排序演算法 的一種,使用 Divide and Conquer 的演算法來實作。其概念是從數列中挑選一個基準點,大於基準的放一邊,小於的放一邊,如此循環最後可完成排序。過程依照以下步驟進行(遞增為例):
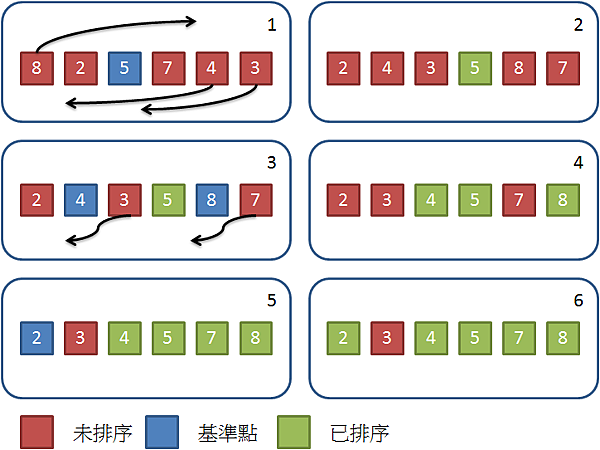
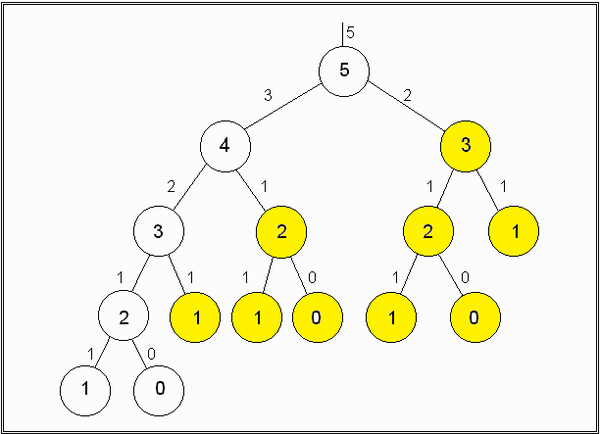
數列中選擇一元素作為基準點 (pivot)。 小於此元素的移至基準的左邊,大於此元素的移至右邊,相等的任意放。 基準點左邊和右邊視為兩個數列,並重複做以上動作直到數列剩下一個或零個元素。 流程範例如圖所示:
實作的方式除了一般使用額外的暫存數列之外,也有使用較少額外空間的 原地 (In-place) 方式,In-place 的方式主要概念是將基準點暫時移到最右邊,小於基準的移至數列一端並記錄遞增索引,最後將基準點換回索引位置,過程依照以下步驟進行 (遞增為例):
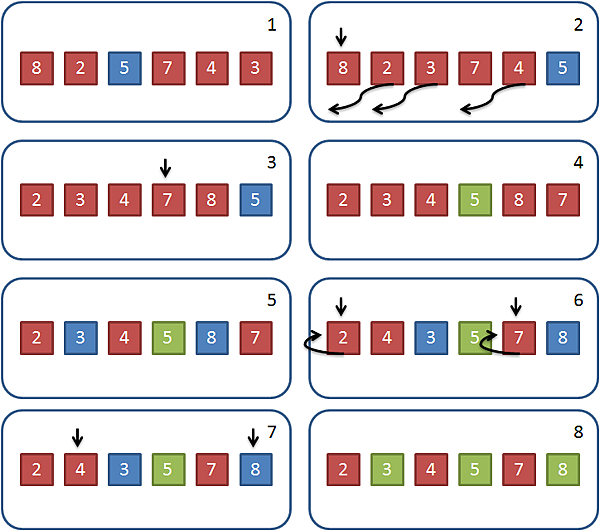
數列中選擇一元素作為基準點 (pivot),並與最右邊的元素交換位置。 建立一索引指向最左邊元素。 小於基準的元素與索引位置的元素交換位置,每次交換後遞增索引。 完成後將基準點與索引位置的元素交換位置。 基準點左邊和右邊視為兩個數列,並重複做以上動作直到數列剩下一個或零個元素。 流程範例如圖所示:
基準點的選擇方式通常直接取第一個元素,在這種方式法的 Worst case 會發生在數列剛好是相反方向排序好的情況下,解決的方法可以改成隨機選取基準點。
除此之外還有其他的變形版本:
Balance Quick Sort:基準點改為取中間的元素。 External Quick Sort Three-way Radix Quick Sort Quick Radix Sort 分析 最佳時間複雜度:O(nlog n) 平均時間複雜度:O(nlog n) 最差時間複雜度:O(n^2) 空間複雜度:一般版本 O(n),In-place O(log n) Stable sort:一般版本是,In-place 不是 虛擬碼 一般版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 function sort(list) if list.length < 2 return list end if pivot = 從 list 取出一基準點 var less, greater, result for i = 0; i < list.length; ++i if list[i] > pivot greater.add(list[i]) else less.add(list[i]) end if end for result.add(sort(less)) result.add(pivot) result.add(sort(greater)) return result end function
In-place版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 function sort(list, left, right) if right <= left return end pivotIndex = 從 list 取出一基準點 pivot = list[pivotIndex] swap(list[pivotIndex], list[right]) swapIndex = left for i = left; i < right; ++i if list[i] <= pivot swap(list[i], list[swapIndex]) ++swapIndex end if end for swap(list[swapIndex], list[right]) sort(list, left, swapIndex - 1) sort(list, swapIndex + 1, right) end function
語法 C# 一般版本 - 物件導向寫法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;namespace QuickSort { class ObjectOriented { static Random random = new Random(); public static void Sort (int [] array { Sort(array.ToList()).ToArray().CopyTo(array, 0 ); } public static List<int > Sort (List<int > list ) { if (list.Count < 2 ) return list; int pivot = list[list.Count / 2 ]; list.RemoveAt(list.Count / 2 ); List<int > less = new List<int >(); List<int > greater = new List<int >(); List<int > result = new List<int >(); foreach (int n in list) { if (n > pivot) greater.Add(n); else less.Add(n); } result.AddRange(Sort(less)); result.Add(pivot); result.AddRange(Sort(greater)); return result; } } }
In-place 版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;namespace QuickSort { class InPlace { static Random random = new Random(); public static void Sort (int [] array { Sort(array, 0 , array.Length - 1 ); } public static void Sort (int [] array, int left, int right { if (right <= left) return ; int pivotIndex = (left + right) / 2 ; int pivot = array[pivotIndex]; Swap(array, pivotIndex, right); int swapIndex = left; for (int i = left; i < right; ++i) { if (array[i] <= pivot) { Swap(array, i, swapIndex); ++swapIndex; } } Swap(array, swapIndex, right); Sort(array, left, swapIndex - 1 ); Sort(array, swapIndex + 1 , right); } private static void Swap (int [] array, int indexA, int indexB { int tmp = array[indexA]; array[indexA] = array[indexB]; array[indexB] = tmp; } } }
Java 一般版本 - 物件導向寫法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 import java.util.List;import java.util.Random;import java.util.ArrayList;public class ObjectOriented { static Random random = new Random (); public static void Sort (int [] array) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <Integer>(); for (int n : array) list.add(n); list = Sort(list); for (int i = 0 ;i < array.length;++i) array[i] = list.get(i); } public static List<Integer> Sort (List<Integer> list) { if (list.size() < 2 ) return list; int pivot = list.get(list.size() / 2 ); list.remove(list.size() / 2 ); List<Integer> less = new ArrayList <Integer>(); List<Integer> greater = new ArrayList <Integer>(); List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); for (Integer n : list) { if (n > pivot) greater.add(n); else less.add(n); } result.addAll(Sort(less)); result.add(pivot); result.addAll(Sort(greater)); return result; } }
In-place 版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import java.util.Random;public class InPlace { static Random random = new Random (); public static void Sort (int [] array) { Sort(array, 0 , array.length - 1 ); } public static void Sort (int [] array, int left, int right) { if (right <= left) return ; int pivotIndex = (left + right) / 2 ; int pivot = array[pivotIndex]; Swap(array, pivotIndex, right); int swapIndex = left; for (int i = left; i < right; ++i) { if (array[i] <= pivot) { Swap(array, i, swapIndex); ++swapIndex; } } Swap(array, swapIndex, right); Sort(array, left, swapIndex - 1 ); Sort(array, swapIndex + 1 , right); } private static void Swap (int [] array, int indexA, int indexB) { int tmp = array[indexA]; array[indexA] = array[indexB]; array[indexB] = tmp; } }
C++ 一般版本 - 物件導向寫法 ObjectOriented.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #ifndef OBJECTORIENTED_H #define OBJECTORIENTED_H #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <time.h> #include <unistd.h> using namespace std;class ObjectOriented { public : static void Sort (int * array, int length) protected : private : static vector<int > Sort (vector<int > list) }; #endif
ObjectOriented.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 #include "ObjectOriented.h" void ObjectOriented::Sort (int * array, int length) srand (time (0 )+getpid ()); vector<int > ivector (length) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) ivector[i] = array[i]; ivector = ObjectOriented::Sort (ivector); for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) array[i] = ivector[i]; } vector<int > ObjectOriented::Sort (vector<int > list) if (list.size () < 2 ) return list; int pivot = list[list.size () / 2 ]; list.erase (list.begin () + list.size () / 2 ); vector<int > less; vector<int > greater; vector<int > result; for (int i = 0 ;i < list.size ();++i) { if (list[i] > pivot) greater.push_back (list[i]); else less.push_back (list[i]); } less = ObjectOriented::Sort (less); for (int i = 0 ;i < less.size ();++i) result.push_back (less[i]); result.push_back (pivot); greater = ObjectOriented::Sort (greater); for (int i = 0 ;i < greater.size ();++i) result.push_back (greater[i]); return result; }
In-place 版本 InPlace.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #ifndef INPLACE_H #define INPLACE_H #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <time.h> #include <unistd.h> using namespace std;class InPlace { public : static void Sort (int * array, int length) protected : private : static void Sort (int * array, int length, int left, int right) }; #endif
InPlace.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include "InPlace.h" void InPlace::Sort (int * array, int length) srand (time (0 )+getpid ()); InPlace::Sort (array, length, 0 , length - 1 ); } void InPlace::Sort (int * array, int length, int left, int right) if (right <= left) return ; int pivotIndex = (left + right) / 2 ; int pivot = array[pivotIndex]; swap (array[pivotIndex], array[right]); int swapIndex = left; for (int i = left; i < right; ++i) { if (array[i] <= pivot) { swap (array[i], array[swapIndex]); ++swapIndex; } } swap (array[swapIndex], array[right]); InPlace::Sort (array, length, left, swapIndex - 1 ); InPlace::Sort (array, length, swapIndex + 1 , right); }
隨機產生 100000 筆資料實測,C++ 意料之外的慢,Java 意料之外的快
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 C# InPlace: 30ms ObjectOriented: 150ms Java InPlace: 30ms ObjectOriented: 180ms C++ InPlace: 380ms ObjectOriented: 2530ms
延伸閱讀 排序演算法 (Sorting) 分治法 (Divide and conquer)