Using Ethers.js to Sign and Recover
Solidity - ecrecover this article explains how smart contracts verify signatures. This article will explain how to use Ethers.js to sign and recover. This article uses Ethers.js version 6.7.1.
Signer
The Signer object will be used in the following content. Here is a brief explanation of how to obtain it.
Private Key
1 | import { JsonRpcProvider, Wallet } from "ethers"; |
Browser Wallet
1 | import { BrowserProvider } from "ethers"; |
Sign
Unlike Web3.js has many methods, Ethers.js has the following synchronous and asynchronous versions:
- signer.signMessage
- signer.signMessageSync
For EIP-712 related methods, refer to Using Ethers.js to Sign and Recover EIP-712 Typed Structured Data.
signer.signMessage
Always use EIP-191 prefix
1 | signer.signMessage(message: string | Uint8Array): Promise<string> |
- message: Content to sing. If it is a string, is treated as plain text, and binary data uses Uint8Array.
- Return: A Promise object, and the content is a signature.
With the prefix, the signing content is
1 | “\x19Ethereum Signed Message:\n” + message.length + message |
For example, sign binary content
1 | import { getBytes } from "ethers"; |
A message will pop up in Metamask as follows: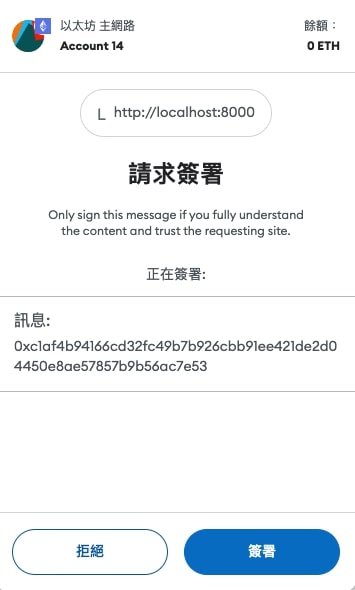
We can use the library to split the signature.
1 | import { Signature } from "ethers"; |
Using prefix in smart contracts:
1 | bytes32 messageHash = 0xc1af4b94166cd32fc49b7b926cbb91ee421de2d04450e8ae57857b9b56ac7e53; |
Or sign plain text content:
1 | const message = 'OK!'; |
A message will pop up as follows: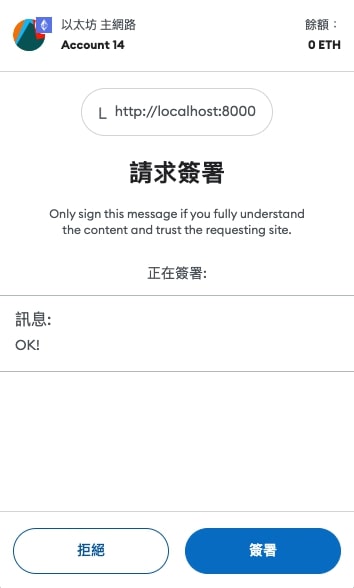
Solidity
1 | string memory message = "OK!"; |
Note that if the text is UTF-8, the length of the signature on the chain must be bytes. For example:
1 | // 6 |
signer.signMessageSync
Synchronous version of signMessage, only available in Node.js
1 | signer.signMessageSync(message: string | Uint8Array): string |
- message: Content to sing. If it is a string, is treated as plain text, and binary data uses Uint8Array.
- Return: signature.
Get the signature directly
1 | const signature = signer.signMessageSync(message); |
Others are the same as signMessage and will not repeat.
Signature Format
The above signature has two formats: Splitted and not splitted. Wee can split it by fixed length. The first 32 bytes are r, the middle 32 bytes are s, and the last 1 byte is v. The example above:
signature: 0xe1077fb9321c187d8a43926896abac5455ce6add269e098f855ff059d6b846a356320be5f6d79c4d0e5583d6b9a2e50fae78f1fb5ff0553541e69c66dae2b2f81b
r: 0xe1077fb9321c187d8a43926896abac5455ce6add269e098f855ff059d6b846a3
s: 0x56320be5f6d79c4d0e5583d6b9a2e50fae78f1fb5ff0553541e69c66dae2b2f8
v: 0x1b
Therefore, in addition to using the method mentioned above to split the signature, we can also simply do it ourself:
1 | function splitSignature(signature) { |
Recover Signature
In addition to verify and recover in smart contracts, we can also use Ethers.js. It can be used as back-end program for login. We can use the following function:
- verifyMessage
- recoverAddress
verifyMessage
The EIP-191 prefix is always used, and plain text or binary data can be entered for the signature content.
1 | verifyMessage(message: Uint8Array | string, sig: SignatureLike): string |
- message: Content to sing. If it is a string, is treated as plain text, and binary data uses Uint8Array.
- sig: Signature. It can be a not splitted string or an object containing vrs.
- Return: Signer address.
Binary data
1 | import { getBytes, verifyMessage } from "ethers"; |
Plain text content
1 | const message = 'OK!'; |
recoverAddress
The EIP-191 prefix is always used, and pm;y binary data can be entered for the signature content.
1 | recoverAddress(digest: Uint8Array | string, signature: SignatureLike): string |
- digest: Signed content, the string must be a string starting with 0x or use Uint8Array.
- message: Content to sing. If it is a string, it must be starting with 0x, or uses Uint8Array.
- sig: Signature. It can be a not splitted string or an object containing vrs.
- Return: Signer address.
Strings starting with 0x can be passwd in directly or converted using getBytes.
1 | import { recoverAddress } from "ethers"; |
Signature Malleability
Ethers.js has no problem with Signature Malleability. A tampered signature will cause an INVALID_ARGUMENT error.
Conclusion
- It is more general to use
signMessagefor signing. - To verify and recover the plain text of the signature, you can use
verifyMessage. - Use
recoverAddressto verify and recover the binary content of the signature.
Further Reading
Solidity - ecrecover
Solidity - Signature Malleability
Using Web3.js to Sign and Recover
Using Ethers.js to Sign and Recover EIP-712 Typed Structured Data


